A sedentary lifestyle, injuries or excessive physical activity cause diseases of the musculoskeletal system. To avoid complications, it is important to start treatment early in the process. To do this, you need to know the causes and symptoms of the pathology.
Description of the disease, what is its danger
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is a chronic disease in which dystrophic changes begin in the cartilage located in the intervertebral space. The pathology is expressed by a decrease in the height of the discs and compression of the intercostal nerve endings.
Thoracic osteochondrosis goes through several stages of progression.
The first is characterized by dryness of the intervertebral disc, decreased firmness and elasticity and the appearance of fissures. The pain is mild and disappears after the person rests for a while.
In the second stage, the disc decreases in height, the vertebra niche is filled by the nucleus pulposus, but does not exceed its limits. Muscles experience constant tension. The person complains of severe pain, which disappears after rest.
The third stage is characterized by the exit of the nucleus pulposus beyond the edges, the fissure reaches the vertebral edge. As a result, an intervertebral hernia is formed. The pain becomes constant.
At the fourth stage, a proliferation of connective tissue is detected, which puts pressure on nearby vertebrae. To compensate for the reduced layer, bone tissue begins to grow. More and more growths (osteophytes) appear.
Types of thoracic osteochondrosis and complications
Based on the nature of the pain, two types of thoracic osteochondrosis are distinguished:
- dorsago, which is characterized by sharp, stabbing pain in the form of low back pain, located in the thoracic spine. The condition is accompanied by muscle tension, problems moving the neck and thoracic region;
- back pain, in which the pain increases slowly. Inhaling and turning the body, as well as remaining in the same position for a long time, increase discomfort. At night, the discomfort deepens and disappears during walking.
In the absence of adequate therapy, nerve endings become increasingly compressed. As a result, osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine can cause complications:
- diseases of the digestive system;
- persistent pain;
- interruptions in cardiac activity;
- decreased ability to conceive;
- disturbance in the functioning of the lungs caused by the proliferation of connective tissue.
Why does thoracic spine pathology occur?
This part of the spine experiences moderate load and limited mobility. However, the pathology is common. The disease can be caused by one of the reasons or a combination of them:
- injuries and damages;
- excessive load on the department, including in childhood;
- age-related changes associated with a decrease in nutrition of the disc tissue between the vertebrae;
- endocrinological diseases, especially during menopause;
- age-related impairment of calcium absorption;
- excess body weight;
- problems with blood vessels, atherosclerotic deposits in the vessels of the thoracic region;
- weak muscular corset.
How does the pathology manifest itself?
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis include pain and increased muscle tone. The pain can be short-lived, with stabbing pain, or long-lasting. The recoil can be felt in the front of the chest, under the ribs and in the shoulder. The pain intensifies when remaining in the same position for a long time.
A characteristic sign of the pathology is sensitivity to palpation of the spinous processes of the thoracic vertebrae.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine are similar to those of other diseases and include:
- discomfort in the heart region, reminiscent of angina pain;
- pain when breathing, shortness of breath, also manifested in pneumonia, tuberculosis, obstructive pulmonary disease;
- pain in the epigastric region, under the ribs, similar to signs of gastrointestinal diseases.
Treatment methods for thoracic osteochondrosis
If you have complaints, contact a neurologist. Therapy includes medication, physical therapy, exercise therapy, and massage.
Doctors prescribe medications:
- means eliminating the source of inflammation in the spine;
- medications to reduce muscle tone and the risk of compression of the sensory roots of the spinal cord;
- neuroprotectors designed to help restore nerve fibers.
The choice and dosage are made by the doctor, who will take into account tolerance to the medication, concomitant pathologies and the patient's weight.
It is important to follow the recommended duration of treatment to avoid relapses. You can buy prescription medicines cheaply from the online store.
The massage must be done carefully, using friction techniques. The areas under the shoulder blades and between the ribs must be carefully treated. For the effect to appear, at least 10 to 15 sessions are needed.
During physical therapy, the emphasis is on exercises that strengthen the muscular corset, neck and lower back.
Ointments and gels with anti-inflammatory effects, warming patches and the Kuznetsov applicator are prescribed locally.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is a degenerative pathology of the vertebrae and discs. Vlasenko Alexander Adolfovich (neurologist, manual therapist with 30 years of experience) talks about osteochondrosis of the thoracic region - symptoms, diagnosis and effective treatment methods.
Why is thoracic osteochondrosis called "chameleon"?
The thoracic spine has a special feature - the ribs are attached to it. Thanks to this, it is less mobile than the neck and lower back. Consequently, osteochondrosis in the thoracic region develops less frequently, according to the principle: "less mobility - less wear". But it develops less frequently - that doesn't mean it's easier. And indeed it is. We're talking about chest pain. Since the area of pain in the thoracic spine coincides with the area of the heart, symptoms are often confused with angina pectoris or myocardial infarction. It is not for nothing that they say about thoracic osteochondrosis that it is a "chameleon". After all, he can pretend not only to have a heart disease, but also a disease of the lungs, liver, stomach, gallbladder or pancreas. And here you cannot make a mistake and ignore a heart attack or other serious illness, for example, pathology of the mammary glands in women. These mistakes are costly, even if everything works out in the end. After all, this can "drive" a person into severe stress. That is why it is very important to find an experienced and knowledgeable doctor who understands everything and distinguishes the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis from other pathologies. Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region are usually divided into two categories - radicular and reflex.
Osteochondrosis symptoms
The manifestations of osteochondrosis will depend on the location and severity of the lesion in the motor segment of the spine. In the initial stage, patients complain of back pain, discomfort, slight limitation of spinal movements, periodic numbness in the arms or legs, headache and fatigue. By starting treatment and changing your lifestyle during this period, the results will not be long in coming and recovery will come quickly.
With severe damage to the intervertebral disc, severe pain, persistent numbness and/or weakness in the arm or leg (depending on the level of damage) occurs. These signs may indicate destruction of the intervertebral disc and the presence of a hernia, making it necessary to immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment.
In the most serious cases, the pain syndrome can be extremely intense, possible dysfunction of the pelvic organs, intense weakness and numbness in the arm or leg. If these signs are present, urgent hospitalization is required to resolve the issue of surgical treatment.
In cervical osteochondrosis, pain occurs in the neck, which can radiate to the shoulder, arm or head, numbness or weakness in the arm, headache, dizziness.
With osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, pain occurs in the chest, radiates to the sternum or scapula, intensifies with breathing and movement, and sometimes there is a feeling of shortness of breath. Patients often confuse this condition with heart pain.
When the lumbosacral spine is affected, the pain is localized in the lower back, intensifies with movement, radiates to the leg or perineum, and numbness or weakness in the leg may occur.
It is necessary to remember that our body is a whole and that the division of osteochondrosis into cervical, thoracic and lumbar is arbitrary. As a rule, the disease develops throughout the spine, but manifests itself in the part that experiences the greatest load.
Root symptoms
They occur due to impact on the nerves leaving the spine.
Spinal nerves
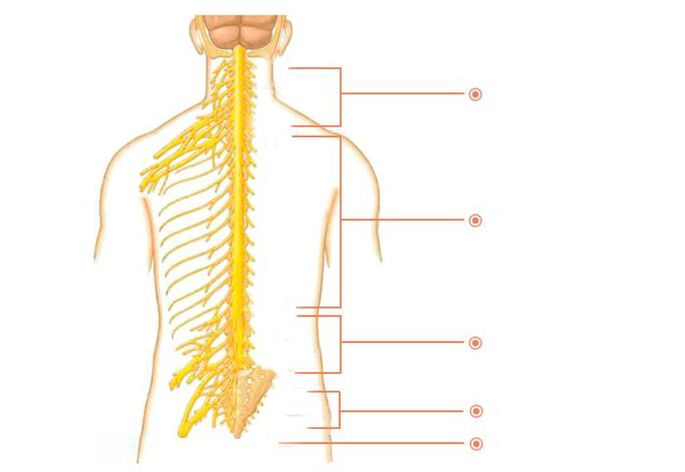
There are many nerves exiting the spine. They are called spinal nerves. Each nerve gradually branches and follows a specific area of the body with clearly defined boundaries. This area is called the segmental innervation zone. Each vertebra, disc, nerve and zone are numbered, corresponding strictly to each other. If a nerve is exposed, symptoms will appear in the segmental innervation zone corresponding to that nerve, and not just anywhere - in an arbitrary location.
Root symptoms include:
- Decreased or lost reflexes;
- Impaired sensitivity;
- Muscle weakness;
- Radicular pain.
Innervation zones of the thoracic segments
Osteochondrosis D1–D2- Causes pain in the shoulder, collarbone and armpit areas.
Osteochondrosis D3–D6- causes pain of a circular nature in the upper part of the chest. Simulates heart pain, an angina attack. In women, it causes pain in the mammary glands.
Osteochondrosis D7–D8- causes pain in the waist at the level of the solar plexus. Simulates pain in the stomach, liver, gallbladder or pancreas. Reduces upper abdominal reflexes.
Osteochondrosis D9–D10- causes pain in the hypochondrium and upper abdomen. Sometimes it imitates the so-called "sharp" abdomen - sharp pain in the abdomen. Reduces mid-abdominal reflexes.
Osteochondrosis D11–D12- causes pain in the groin area. Simulates pain in female diseases, appendicitis and intestinal diseases. Reduces lower abdominal reflexes.
Reflex symptoms
Unlike radicular symptoms, reflex symptoms do not have clear boundaries. These can be: difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, pain when inhaling and exhaling, chills and "goosebumps" on the skin, intercostal neuralgia, chest pain. Dyspepsia is often observed - appetite worsens, nausea, heartburn, bloating and intestinal dysfunction occur. Because of the pain, sleep is disturbed, insomnia occurs and the feeling of not getting enough sleep occurs. It's difficult to move around, especially in the morning. Coordination of movements is impaired - this is reflected in gait. General weakness, weakness. Sexual disorders. Irritability. Rapid fatigueability. Various pains arise. Pressing pain in the chest region. Pain between the shoulder blades. Pain in the hypochondrium. Pain when lifting the arms. Pain when bending over or trying to stand up. Pain between the shoulder blades. In general, pain in osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is usually divided into two types.
back pain- moderately intense and prolonged pain in the back and chest with periods of intensification and attenuation.
Dorsago- acute painful "lumbago" in this area.
- Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region depend on the stage of osteochondrosis.
- They get worse when they bend over or try to stand up.
- Symptoms usually appear after 35-45 years.
- They occur approximately 3 times more frequently in women than in men.
You, of course, noticed that radicular symptoms are defined quite clearly, while reflex symptoms are very vague and nonspecific. And as you know, everything that does not have clear definitions serves as a convenient cover for professional helplessness. This applies, among other things, to reflex symptoms and such a favorite concept among doctors as "age-related changes". Surely many of you are familiar with the situation when the doctor explained the problem as "reflex" or "age-related" processes. Most people at such moments rightly believe that the doctor simply cannot understand what is happening and is trying to hide his incompetence in the fog of these "magic words".
There was a time when there was a popular phrase: "Every accident has a name, surname and position". Therefore, each disease has its unique symptoms. And it is the doctor's duty to know them clearly. And then there will be no need to confuse and blame osteochondrosis of the thoracic region for everything. Now you understand how important it is to find an experienced and knowledgeable doctor. Both the correct diagnosis and good treatment results will depend on this.
Stages of the disease
Depending on the ongoing pathological processes, there are 4 stages of development of thoracic osteochondrosis:
| Internship | Changes | Symptoms |
| First | Dehydration of the discs, which causes loss of elasticity. Its height decreases, but its width increases - the intervertebral disc gradually flattens. | The pain appears directly from the damaged ring. It can be pulling or throwing. |
| Second | The fibrous ring begins to disintegrate. The nerve roots are compressed, causing pain. | There is pain when moving. When maintaining a posture for a long time, discomfort arises. |
| Third | The fibrous ring ruptures, causing a herniated disc to form. Scoliosis or pathological kyphosis develops. | There is pain when moving. When maintaining a posture for a long time, discomfort arises. |
| Room | Friction of the vertebrae appears against each other, which causes displacement of the intervertebral joints. The tissue around the vertebrae becomes inflamed. Cartilaginous tissue is replaced by bone tissue, which reduces motor functions. Fibrosis appears. | There is pain when moving. When maintaining a posture for a long time, discomfort arises. |
Exacerbation and remission stages may be observed. The latter is often observed in stage 4.
Degrees of the disease
This is a more modern classification of the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, used by specialists.
| Degrees | Changes and symptoms |
| First | Intervertebral disc rupture caused by sudden movement or excessive exertion. Sharp pain, similar to the passage of electrical current along the spine. Muscle tension. |
| Second | Characterized by spinal instability. Pain when moving. Protrusion. |
| Third | The pain becomes constant. Loss of sensation. Change in gear. Severe headaches. Difficulty breathing. Tachycardia. |
| Room | The spine is unstable: the vertebrae slip and twist. Osteophytes grow, compressing spinal nerves and putting pressure on the spinal cord. |
Thoracic osteochondrosis can cause serious illnesses that are difficult to cure.
Diagnosis is the key to appropriate treatment
Today, there are several modern methods for hardware diagnosis of osteochondrosis. The most accurate of them are MRI and CT. But the main method is still clinical diagnosis - this is when an experienced doctor compares data from at least three sources - from the patient's complaints, from the results of MRI and from the symptoms that were identified during the examination. This allows you to make a diagnosis as accurately as possible and create an effective individual treatment program.
Who to contact, methods of examining osteochondrosis
As a rule, with back pain, patients turn to a neurologist, who, based on complaints and neurological examination, can make a preliminary diagnosis, prescribe additional examination methods (spine x-ray, MRI, computed tomography, general urinalysis , general blood test) and develop a treatment regimen .
Treatment
Treatment must be comprehensive, aimed at:
- elimination of pain syndrome;
- elimination of impaired function of spinal roots;
- prevention of the progression of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the structures of the spine.
During the acute period, with severe paindrug treatment is prescribed: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, B vitamins, chondroprotectors or blockade are used.
Physiotherapyis the main method of conservative treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Exercise therapy is aimed at the formation, correction and strengthening of the muscular corset; increased range of motion in the spine and joints; development of a motor stereotype and correct posture; reducing the load on the spine.
With regular exercise therapy, joint exercises, yoga or swimming, blood supply and tissue nutrition improve, metabolism is normalized and the intervertebral space increases, which leads to recovery.
Listen to your body, if you encounter symptoms of osteochondrosis or your lifestyle involves sitting at a computer for a long time, driving a car or insufficient physical activity, seek help from a specialist without waiting for exacerbations.
As you understand, osteochondrosis is a real "tangle" of symptoms that, having unraveled, the doctor will relieve you of pain and torment. But it is not possible to eliminate changes in the vertebrae and discs. Therefore, the words "treatment of osteochondrosis" must be understood correctly. If you are interested in eliminating pain and other suffering, then yes, it is quite possible. And if you conduct an academic discussion on the topic of returning vertebrae and discs to their original appearance, "like a newborn child", then no, the past cannot be returned. You need to be realistic and you will not fall for scammers.
Which treatment method is considered the main one?
Gentle manual therapy is the main type of treatment for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region. It's like an antibiotic for pneumonia – you can't live without it. The remaining types - massage, medication, physiotherapy and physiotherapy - are auxiliary.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy methods relieve swelling and inflammation, improve blood flow to the affected area, and reduce or stop pain.
Magnetic laser, magnetic therapy, SMT with novocaine, ultrasound with hydrocortisone, etc.
Balneotherapy: Mud applications, ozokerite applications in affected areas, radon baths.
Exercise therapy and massage
Therapeutic exercise is the main method of treating osteochondrosis. Gymnastics is performed regularly for 10-15 minutes several times a day. To increase effectiveness, a massage course is prescribed. The procedures help relax muscles, reduce pressure on the vertebrae, improve metabolic processes and blood flow. Physiotherapy can be carried out independently at home, as well as in a clinic (individual and group classes). The massage is performed by a qualified specialist in a clinical setting.
How does gentle manual therapy work?
The nutrition of the discs is directly related to the muscles that surround the spine. In addition, the back muscles themselves are one of the constituent causes of pain in osteochondrosis of the thoracic region. Gentle manual therapy is a special method that allows muscles to return to their natural physiology, eliminate spasms, muscle tension and improve disc nutrition.
The intervertebral discs are the only part of the body that does not have blood vessels and are nourished by the proper functioning of muscles.
Additionally, when performing hand treatment, the chiropractor:
- will relieve the load from the affected vertebrae and discs and distribute it correctly;
- relaxes muscles and helps them return to normal;
- relieves the patient of clamps;
- improve disk power supply;
- will restore the body's motor functions;
- normalizes blood circulation.
Manual influence mobilizes the body's internal forces and triggers self-healing mechanisms.
Acupuncture
The technique consists of influencing biologically active points on the body with fine needles. The procedure reduces the manifestation of pain and inflammatory processes. Acupuncture is not painful and minor discomfort may occur.
Treatment of pathology in women
It is virtually impossible to completely get rid of already progressing thoracic osteochondrosis, but it is quite possible to slow down or even stop the formation of a pathological degenerative-dystrophic process in the tissues of the motor segments of the spine using the means and methods of modern medicine. The optimal therapeutic effect can only be achieved with an integrated approach to the treatment of this pathology using medications, various physiotherapeutic techniques and targeted techniques of exercise therapy (physiotherapy).
Symptoms and treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine in women are not much different from those in men. In the acute period of osteochondrosis of the thoracic segment of the spine, the patient needs intensive exacerbation treatment, during which various medications and physical procedures are used that help eliminate, first of all, the pain syndrome and, in parallel, other negative manifestations of illness.
During remission, the patient must receive maintenance treatment, based mainly on the use of medications that restore the osteochondral structure and physiotherapy. In especially severe cases, they sometimes resort to surgical intervention to stabilize the position of the spine.
What to do in case of an exacerbation?
During an exacerbation, intense pain appears, radiating along the intercostal spaces. At this stage, it is necessary to maintain bed rest and reduce spinal mobility. Symptoms are eliminated with painkillers prescribed by the attending physician.
The treatment is absolutely safe.
Prevention
To prevent diseases and slow down degenerative processes, it is recommended:
- weight adjustment;
- cycling, running, swimming, yoga and other sports;
- daily walks;
- take vitamin and chondroprotective complexes;
- reducing stress on the back;
- timely treatment of musculoskeletal diseases.
To avoid relapses, create comfortable conditions for sleeping and working. Watch your weight and eat well. Continue with your physical activity. But the main thing is not to neglect your health and not save on it. Don't let things take their course. After recovery, try to have at least one maintenance session of gentle manual therapy once every three to six months - this will reduce risk factors. Do not forget, advanced osteochondrosis leads to complications - protrusion and herniated discs. Remember: your health comes first!



















